Force Formulas
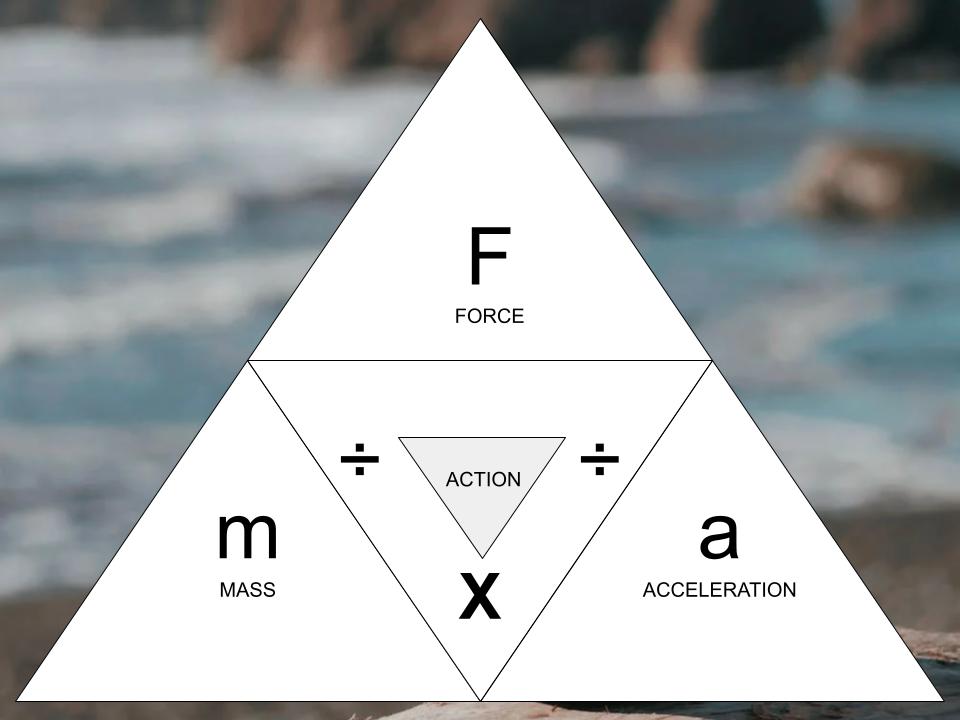
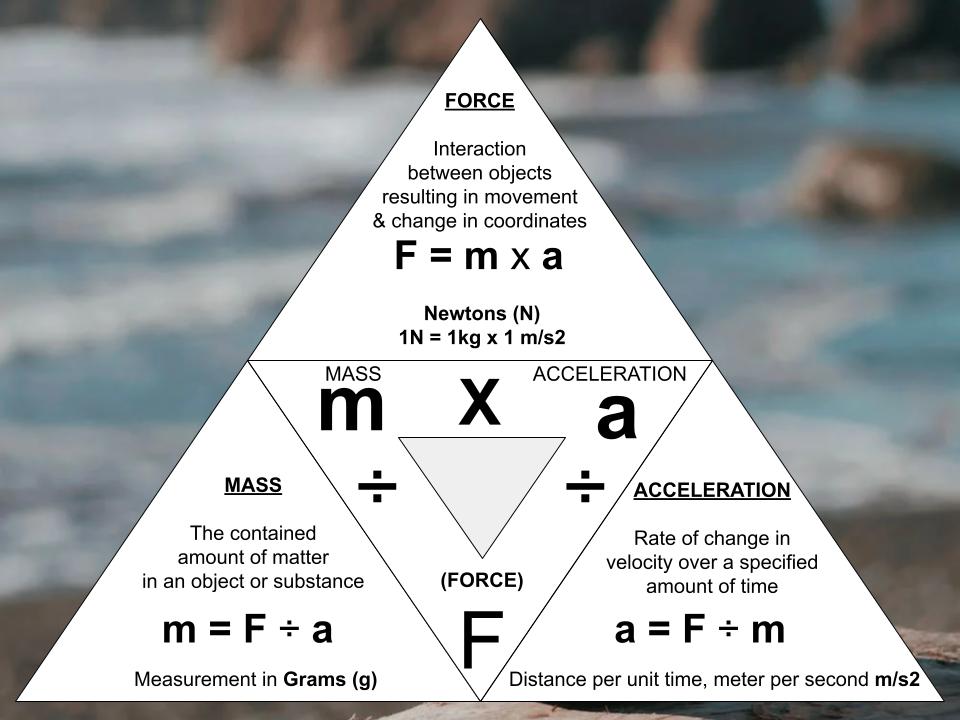
The acceleration, force, and mass of an object are related by the equation “net force = mass x acceleration”. If you know two of these values, you can solve for the third using this equation.
To calculate the net force of an object, multiply the mass of the object (measured in grams) by its acceleration (measured in meters per second squared).
To find the acceleration of an object, divide the net force (measured in Newtons) by the mass of the object.
To workout the mass of an object, divide the net force by the acceleration.
These formulas give the force of energy due to the position of mass and motion relative to other objects that provide motion energy.
Movement by Net force
Displacement of an object with mass changes its Potential force and enables harvesting of kinetic energy to produce electricity
When an object with mass is moved to a different position or configuration, the net force calculations are altered.
More research:
Video explaining Kinetic energy. Part 2 – Energy, Work & Power,
KE or PE – Different types of energy.