Kinetic energy
The motion of an object with mass is measured by the kinetic energy equation.
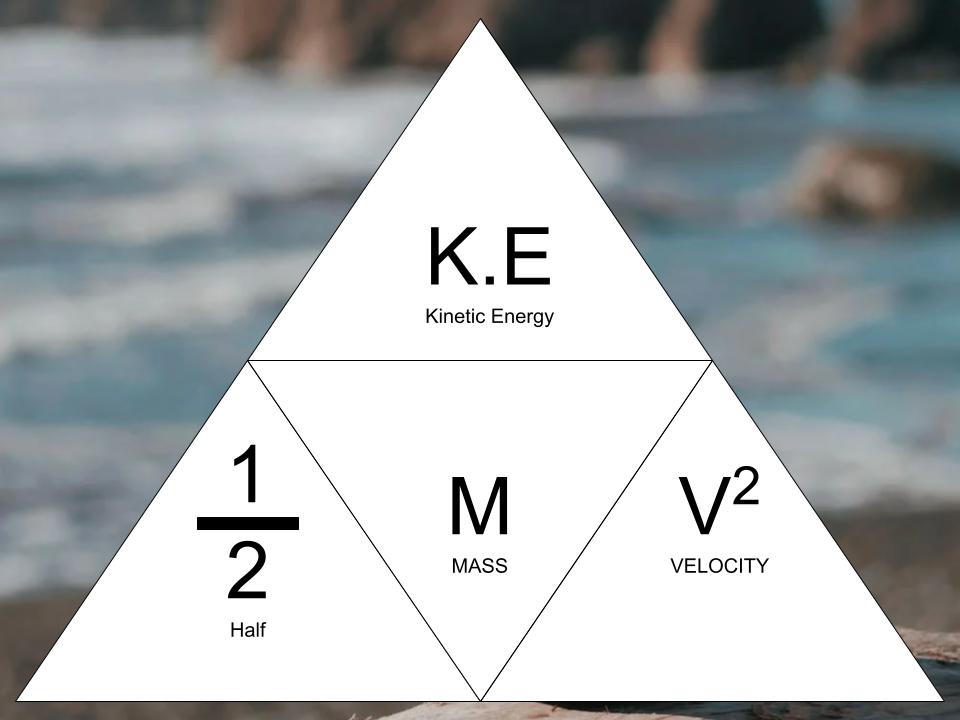
Formula: K.E. = 1/2 m v2
Kinetic energy can be described as work in motion, however this differs to the work done for motion energy.
Kinetic Electricity
Harvesting kinetic energy to produce electricity has almost exclusively been provided by steam driving an alternating current from a motor. It is this motor method that has been replaced in technology developed by Active Kinetic 1 machines.
Is anything moving kinetic energy?
Yes anything in motion has kinetic energy.
Is it true that a moving object can have no kinetic energy?
Yes, that’s correct. Anything in motion has kinetic energy, unless its motion is negligible or at rest relative to its surroundings. Kinetic energy is a property of an object’s motion, and it’s directly related to its velocity. If an object is stationary or moving at almost the same speed and direction compared to its surroundings, its kinetic energy is considered negligible or practically zero.
For example, if you’re sitting in a chair, you have some kinetic energy due to the Earth’s rotation, the Earth’s orbit around the Sun, and other such motions. However, because these speeds are so vast compared to our everyday experiences, the kinetic energy associated with them is usually considered insignificant for most practical purposes. On the other hand, if an object is moving significantly relative to its surroundings, it will have measurable kinetic energy.
Using kinetic energy.
Pulsatile Kinetic Energy is the most common format for natural sources of kinetic energy. Active Kinetic 1 technology provides a transformational resource to access forms of kinetic energy that have been challenging for traditional electric generating mechanisms that struggle to harness useful amounts of energy. The ocean is a good example where traditional generators don’t produce much power.
Kinetic motion technology unlocks the ability to easily and reliably access this kinetic energy and convert it into electricity wherever in the universe we find movement.
What is the equation for kinetic energy?
The mass of an object and it’s square velocity is used to calculate Kinetic energy using this equation: K.E. = 1/2 mv2
Translating the physics equation: Kinetic energy = 1/2 (half) Mass x Velocity squared.
More research:
Video explaining Kinetic energy. Part 2 – Energy, Work & Power,
KE or PE – Different types of energy. Potential energy